 Achieving optimal performance of solar control low-e glass and passive low-e glass requires proper placement of low-e coatings on the glass surfaces of an insulating glass unit (IGU). Placement considerations vary depending on whether the glass is solar control low-e glass or passive low-e glass, and whether the IGU is double- or triple-glazed.
Achieving optimal performance of solar control low-e glass and passive low-e glass requires proper placement of low-e coatings on the glass surfaces of an insulating glass unit (IGU). Placement considerations vary depending on whether the glass is solar control low-e glass or passive low-e glass, and whether the IGU is double- or triple-glazed.
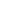
For double-glazed IGUs using solar control low-e glass, orient the coating on the inside of the outward most (building exterior) lite—the second surface—of the IGU. The addition of argon gas or a second low-e coating on the 4th surface will further improve performance.
For triple-glazed IGUs using solar control low-e glass, orient the low-e coating on the second and fourth surfaces of the IGU. Here, the addition of argon gas or a third low-e coating on the 6th surface will improve performance slightly.
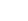
For double-glazed IGUs with passive low-e glass, orient the coatings on the surfaces of the inward most (building interior) lite of glass. Similar to solar control low-e glass, the addition of argon gas or a second low-e coating on the 4th surface will improve performance.
For triple-glazed IGUs with passive low-e glass, Orient the passive low-e coating on one of the surfaces on the inward most lites of glass. To improve performance slightly, add argon gas or a third low-e coating on the 6th surface.
Updated on September 2, 2025