While aesthetically versatile and offering outstanding performance, working with glass does come with some special considerations. This is especially relevant in commercial architecture, where it’s common to specify large glass panels to achieve a dramatic look. A thermal stress break is one such issue.
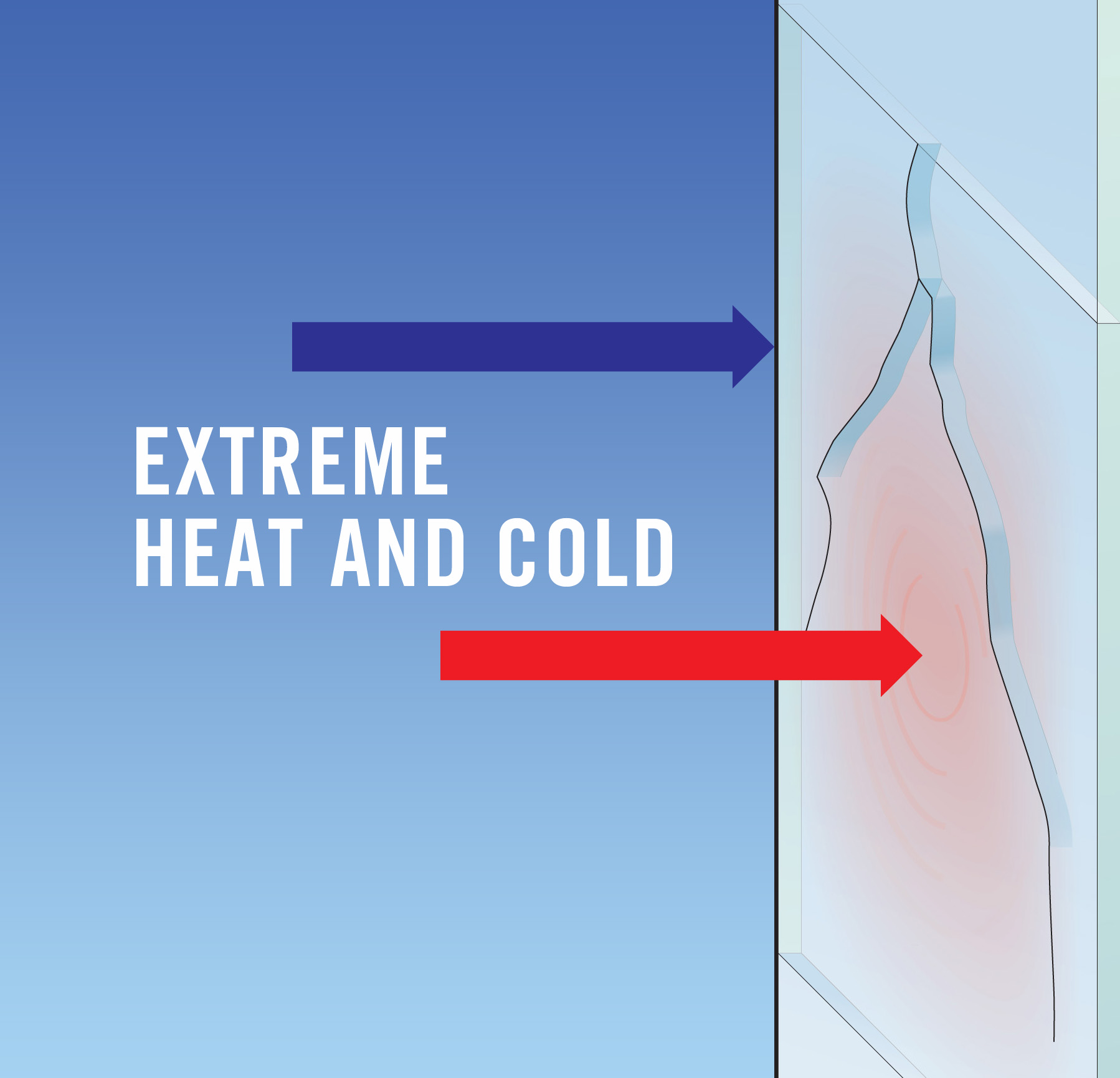
A thermal stress break occurs when the center of the glass in a window unit becomes hotter than the edge of the glass that is inside the framing, causing the center to expand. The resulting tensile stress placed on the glass edges can exceed the strength of the glass, causing the glass to break at a 90-degree angle in from the edge.
 That’s why Vitro Architectural Glass (formerly PPG glass) always recommends working closely with the fabricator, and having a thermal stress analysis completed at the beginning of the design phase. Vitro glass has developed a thermal stress analysis tool that can be used by anyone. Working this simple analysis into the design process helps ensure the right glass is being used for a project’s anticipated thermal stress loads.
That’s why Vitro Architectural Glass (formerly PPG glass) always recommends working closely with the fabricator, and having a thermal stress analysis completed at the beginning of the design phase. Vitro glass has developed a thermal stress analysis tool that can be used by anyone. Working this simple analysis into the design process helps ensure the right glass is being used for a project’s anticipated thermal stress loads.
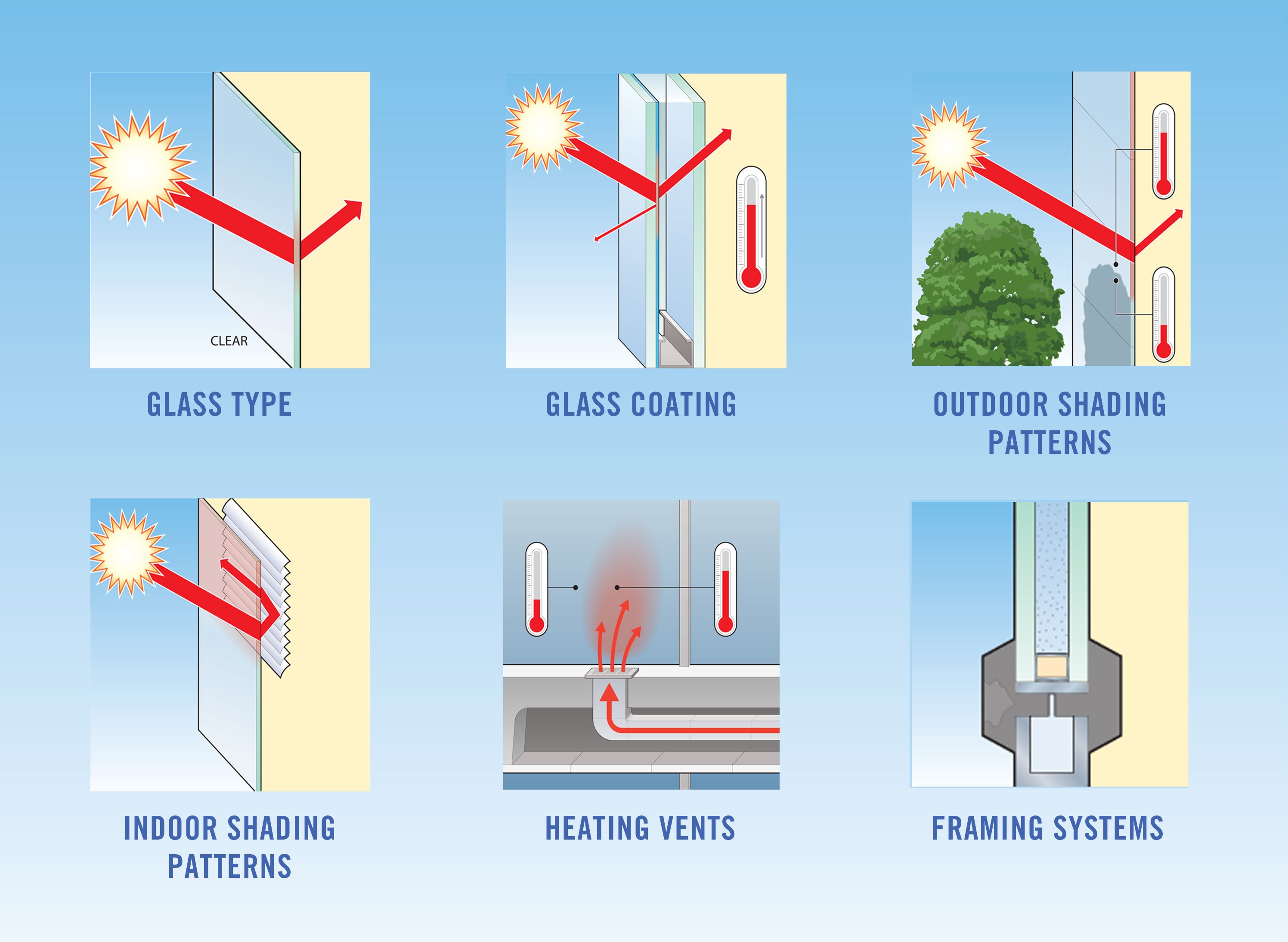
Other factors that can impact glass and its ability to resist a thermal stress break include:
- Glass Type: Glass is available in a wide range of colors, from ultra-clear to the deepest gray tint. Tinted and spectrally-selective glasses absorb solar radiation and heat up. This absorption makes tinted glasses more susceptible than clear glasses to break due to thermal stress.
- Coating Type and Location: Reflective and low-e coatings both reflect and absorb solar radiation, and depending on their surface location in an IG, can increase the amount of solar radiation absorbed by the outer (or inner) pane of glass and change the associated thermal stress risks.
- Outdoor Shading Patterns: This is one of the most dynamic elements since shading patterns vary seasonally. One way to deal with this factor is to minimize locations within your project where less than 50% of the glass panel is covered with shade. This will help avoid temperature gradient extremes.
- Indoor Shading Devices: Just as outdoor shading patterns can impact the thermal load put on glass, indoor shading devices, such as blinds or drapes, can also increase the temperature of the glass. This occurs when the blind or shade reflects the solar radiation back through the glass, reducing the convection and conduction of the heat away from the glass.
- Heating Register Location and Orientation: In any building, the registers need to be carefully placed in order to ensure that warm air isn’t being directed at the glass, which can cause the glass to heat up and lead to breakage.
- Framing System: Look for a framing system that has a low heat capacity as one more way to minimize the chance of a break.
All of the above factors can increase or decrease the likelihood that a window will experience a thermal stress break, and again why Vitro glass strongly recommends working closely with your glass fabricator and getting a thermal stress analysis done early in your design process. Vitro glass has developed a thermal stress analysis tool for insulating glass units (IGUs) that can be used by anyone. It’s a simple calculation that can help you reduce the risk that the glass units you specify will experience a thermal stress break. If your analysis indicates your glass selection is at risk for greater than eight thermal stress breaks per 1,000 units, you can adjust your design to address your risk or consider using heat-treated glass instead.
For complete technical information about thermal stress, read Vitro Architectural Glass Technical Document TD-109. For any other glass questions, please contact Vitro glass or call 1-855-VTRO-GLS (1-855-887-6457).
Updated on August 20, 2024